WEBINAR on “GIS Application: How GIS is changing the world?”.
Date: May 14th, 2022


By: Akshat Agarwal
The concepts of taste and satisfaction are familiar to all of us. It is very difficult to express these concepts in concrete terms. For example, say, one has just eaten an ice-cream and a chocolate. It is now very difficult for that person to say out of these two commodities which has satisfied him more. Similarly it is very difficult to say that how much the consumer likes one over the other. It is evident that we need more quantitative measures of satisfaction. Due to these reasons, the economists developed the concept of utility.
MEANING OF UTILITY:
Utility refers to satisfaction generated by the usage of a commodity.
HOW TO MEASURE UTILITY?
According to classical economists, utility can be measured in the same way as weight or height is measured. Economists assume that utility can be measured in cardinal terms. By using cardinal measure of utility there is no standard unit of measuring utility. So economists derived an imaginary measure of utility which is expressed in terms of psychological units.
MARGINAL UTILITY:
Marginal Utility is the additional utility derived from the consumption of one more unit of the given commodity.
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as we consume more and more units of a commodity, the utility derived from each successive unit goes on decreasing. This means that after a certain period of time due to repeated use of the same commodity, the utility of the consumer will come to an end. This is a challenging situation if looked from the standpoint of a businessman selling that particular commodity. So following are some ways by which a businessman can delay that stage when utility becomes zero and increase utility of the consumer.
PRICE ALTERING:
When prices come down there is an increase in the demand of a commodity. It has to be remembered that demand is connected to utility. If a commodity has no utility then there will be no demand for it. So an increase in demand generally indicates towards an increase in utility.
To push demand up, a businessman may lower the price of a commodity, thereby increasing the utility of it and increasing the sales of it. Say, for example, a customer came to a shop to purchase 2 T-shirts, each costing Rs. 100. So the customer wanted to spend Rs. 200. Now the shopkeeper gives him an offer of purchasing 2 additional T-shirts at Rs. 50 each. Thus, now the customer can buy 4 T-shirts by spending Rs. 300.
Here, by price altering the businessman increased the demand of the customer and also influenced the utility levels of the customer. However, this may not necessarily be the case, in case of all types of commodities. If the commodity concerned here, would have been a perishable commodity, then even when offered a low price for an additional amount of it, the customer would have refrained from purchasing it.
CUSTOMER HANDLING:
Say, there are two shops side by side. In one of the shops the salesman is lazy and sleepy. So he does not treat the customers nicely. But in the second shop, the salesman treats the customers very politely. The question that arises in this context is that from which shop the customers will prefer to buy commodities. The answer is obviously, the second shop. So nicely treating the customers will help the second shop to combat the problems arising from diminishing marginal utility.
PEOPLE DON’T LIKE TO BE SOLD, THEY LIKE TO BE HELPED:
People don’t like to be sold. This means that the sales personnel have to understand the problem of the customer. He/ she have to take care of the need of the customer. Just selling the goods will not help the purpose. The problems of the customer will have to be solved. In the process, the product has to be sold so that a good impression is created in the mind of the customer. This will ensure repeated visits of the customer in future also.
INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY:
It is important to bring a change in the product from time to time and that change should be in the form of innovation. In this case, technology can be used to bring about these innovations. Here an example of a food business can be cited. Suppose a customer comes to a food selling shop and consumes five pieces of a confectionery item. With every additional piece of consumption his marginal utility is going down. And after a certain point of time his marginal utility becomes zero. In such a case, if he is served with another vertical of the product or an innovated version of the product. Then probably he will start to enjoy having that commodity and his marginal utility will start going higher again.
CROSS SELLING:
Cross selling is the model of the business in which the businessman sells his/ her commodity with other commodities. For example, there are popular eatery brands that operate around the world. They sell burgers at twenty five rupees in India. At a certain point of time, it was seen that consumers’ marginal utility was affecting their business. They redesigned the way their products were presented in front of the customers. Burgers, which are mainly eaten as a snack in this country, were now presented in front of customers with French Fries and aerated drinks. Thus, a snack was converted into a meal. As a result, sales increased once again. This was a great example of cross selling tackling marginal utility.
FUTURE:
The prices of most commodities are not constant. They fluctuate from to time. Examples of such goods include gold, silver, real estate etc. Say, there may be a situation in near future where the supply of such a commodity is going to get decreased. That is surely going to impact the demand for that commodity. In this case, demand is expected to go down. Under the circumstances, the consumer would prefer to purchase the commodity right now. This is because in near future when the supply of the commodity would go down, its price will increase and demand will decrease. Thus, utility value of a commodity also depends on what is going to happen in future.
BRANDING & ADVERTISING:
Branding and advertising plays an important role. As branding and advertising influence demand, thus it will not be wrong to say that they also influence utility.
Thus, from what has been stated above it is clear that marginal utility will continue to come down and that is inevitable. But some measures can be taken by the entrepreneur to delay that phase.
AUTHOR’S PROFILE:
The author is an eleventh standard commerce student from Salt Lake City, Kolkata. He wants to be an entrepreneur after completion of his bachelor’s degree in commerce.
By: Anamitra Roy
Non-technically speaking, the Indian Companies Act is that act which deals with the formation and functioning of companies.
According to Section 2(20) of the Indian Companies Act, 2013, “Company means a company incorporated under this act or any other previous act”. The journey of this act started in the year 1956. Then this act was amended in 2013. It is administered by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India. In this act for the first time a new concept was introduced which came to be known as Corporate Social Responsibility. According to Section 135 of this act, a company needs to spend 2% of its profits on socially responsible projects. But this is applicable on the company only when it has a net worth of Rupees 500 crores, or a turnover of Rupees 1,000 crores or more, or a net profit of over Rupees 5 crores. A socially responsible project means a project that aims at social development or community development. A new act has been passed by the ministry. This is called Companies 1st Amendment Act 2015. Subsequently came Companies 2nd Amendment Act 2017. This came into effect from 22 January, 2018. This act covered 93 sections which put an effect to make changes in 107 sections of the Companies Act, 2013. After this arrived the Companies 3rd Amendment Act, 2019.
There are broadly two branches through which the ministry works. These are the regional Directors and the Registrar of Companies. At present in India there are 7 such Directors and 22 Registrars of Companies.
The types of companies included in this act are as follows:
A sole proprietorship has been formed and is run by one individual. No other person has anything to do in the decision making process of this type of an organization.
2. Partnership
In a partnership, the liability is to be taken jointly by the partners. There may be two types of partners in this type of an unit. The active partners invest and take part in the daily operations of the unit. On the other hand, the inactive partners only invest and do not take part in the daily operations of the unit. Such inactive partners are also known as sleeping partners.
3. Limited Liability Partnership
In this type of a company the liability of the partners is limited.
4. Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
These are businesses owned by family members jointly and these families follow Hinduism as their religion. But there are also exceptions to this law. Even though Jains and Sikhs are not considered as Hindus, yet they can come under the heading of Hindu Undivided Families.
5. Cooperative
Cooperatives may be defined as union of individuals who have been united because of some common social, economic and cultural needs and aspirations. Cooperatives are jointly owned by the members. They have a democratic set up.
6. Dormant Company
A dormant company is a company which is dormant now but has been formed with the objective of participating in some future projects.
7. Family Owned Business
A family business is a business whose ownership and control lies with the family members. Such businesses are passed on to the future generations of the family.
8. Private Limited Company
A private limited company is a company that has a minimum of 2 shareholders and a maximum of 2,000 shareholders. But these shares have been offered to the insiders. No outsiders can be allowed a share of this company.
9. Small Company
A company other than a public company whose paid up share capital is not more than 50 lakhs may be considered as a small company.
10. Limited Company
11. Public Sector Undertakings
Major shares of such an organization are owned by the government, any state or central government of India. Most of such business units are formed by special ligislations passed by the governments.
12. One Person Company
It is a private company which can have only one director or member.
13. Unlimited Company
A company where the liability of the shareholders is not limited is an unlimited company.
14. Incorporated Company
Section 166 of the Companies Act lists the duties of the directors of the companies. There have been many debates and arguments in the field of law for mentioning specifically the duties of the directors. A group of experts have argued that there may be conflict of interests hampering the directors from rendering their duties. That is why there was a need to specifically write about their duties.


By: Anamitra Roy
Science City, Kolkata, India, is one of the largest science centres in the world and easily the largest in the Indian sub-continent. It is managed by National Council of Science Museums, Ministry of Culture, Government of India (GoI). It started its journey on 1 July, 1997.
In the early 90s it was seen that European countries were expanding their museums and including science experiences as a part of their attraction packages. Following that trend in European countries, GoI came up with this project to promote science and interest on science experiences. The project commenced in 1993 but the gate was opened for visitors in 1997. Today Science City provides visitors with two main facilities. These are Science Centre and Convention Centre. The Science Centre complex comprises of Space Odyssey, Dynamotion Hall, Science Exploration Hall, Maritime Centre, Earth Exploration Hall and Science Park. What is the most unique part of Science City is that it was built up on a garbage disposal venue which was used for this purpose for the last 100 years or so.
The Convention Centre has an auditorium with a seating capacity of more than 2,000 people, a small auditorium of more than 350 seating capacity, many similar small halls and an open air space of more than 20,000 sq. m.
The Space Odyssey comprises of the 3D Digital Theatre, 3D Theatre, Time Machine and Reflections. The 3D Digital Theatre is a first of its kind in India. It was built up in tune with some of the most advance theatres in the world. Movies shown here include “The Life of Trees” and “Asteroid: Mission Extreme”. Usually these movies are of about half an hour. They are educative. The complicated matters of science have been presented in these movies in a simple form so that it is easily understandable by all. In the section of Reflections one can see 22 exhibits of different types of mirrors like plain, convex and concave. Some other amazing pieces of installation include a mirror maze where even the cleverest of the people can lose their sense of direction. There is also a mirror that reflects images upside down.
The Dynamotion Hall in this Science City comprises of aquariums, butterfly enclaves, nano labs and many others. The aquariums have more than 1,000 varieties of fish from around the world that includes the Piranhas from Brazil, the Oscars, the Angels, Silver Dollars, Red Sharks, crocodiles etc. In the butterfly enclave one can see different types of butterflies. It produces an excellent opportunity to study the lives of butterflies, how they collect nectar and how they lay eggs. The purpose of having the nano labs was to present nano science to the common people. In these labs students are encouraged to take up assignments and projects. They can work during their holidays or during weekends.
The Science Exploration Hall depicts history of formation of Earth, origin of life, evolution of life, human species and their migration patterns etc. Pre-historic human skulls recovered from original fossils are displayed here for the common people.
The Maritime Centre has been developed in association with Kolkata Port Trust. It depicts stories related to history and development of marine science, marine activities, models of boats, ships, frigates etc. The building itself looks like that of a ship. It is a two storied building that covers about 700 sq. m.
The Earth Exploration Hall was opened to visitors on 6 December, 2008. A huge globe is situated in the middle of the hall. With the help of multimedia presentations, major issues related to the earth and solar system are showed here. Usually the show goes on for about half an hour. There is an anchor who speaks live during the show. Beside this there is a 3-D theatre where viewers can watch 3-D movies on science related matters.
Apart from this, there are other attractions of this science centre. One can travel across the open areas through cable cars (or ropeways). The food stalls serve food from different parts of India and the world. It can be a perfect place for a day out in Kolkata. Having said that, it has to be remembered science centres like this do not guarantee progress of the visitors. The main purpose of such science centres is to display the complicated matters of science in a simple form. This is done so that the visitors can generate interest in these matters, they can develop a scientific way of thinking; can start to think of science as a partner in their advancement.
Science City, Kolkata, India, is a wonderful effort by the Government of India. The neatly maintained park is a matter of national pride. The friendly staffs of this science park, periodical lectures and sessions with eminent scientists and lecturers of science and science shows are additions to this park.
Profile of Author:
The author is an alumnus of University of Wales, U.K. He is a frequent visitor to Science City, Kolkata, India.

Vikash Kumar Prasad
According to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, marginal utility of a good diminishes as an individual consumes more units of a good. In other words, as a consumer takes more units of a good, the extra utility or satisfaction that he derives from an extra unit of the good goes on falling.
It should be carefully noted that is the marginal utility and not the total utility that declines with the increase in the consumption of a good. The law of diminishing marginal utility tells us that the total utility increases but at a decreasing rate.
Breaking Down “Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility”:
Marginal utility may decrease into negative utility, as it may become entirely unfavourable to consume another unit of any product. Therefore, the first unit of consumption for any product is typically highest, with every unit of consumption the volume of utility comes doqwn. Consumers handle the law of diminishing marginal utility by consuming numerous quantities of numerous goods.
Diminishing Prices:
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility directly relates to the concept of diminishing prices. As the utility of a product decreases as its consumption increases, consumers are willing to pay smaller prices for more of the product. For example, assume an individual pays Rs.10000 for a vacuum cleaner. Because he has little value for a second vacuum cleaner, the same individual is willing to pay only Rs. 2000 (say) for a second vacuum cleaner. The law of diminishing marginal utility directly impacts pricing because the price charged for an item must correspond to the consumer’s marginal utility and willingness to consume or utilize the good.
Example of Diminishing Marginal Utility:
An individual can purchase a packet of biryani for Rs.200; she is quite hungry and decides to buy five packets of biryani. After doing so, the individual consumes the first packet of biryani and gains a certain positive utility from eating the food. Because the individual was hungry and this is the first unit of the food she consumed, the first packet of biryani brings her a high degree of benefit. Upon consuming the second packet of biryani, the individual’s appetite is getting satisfied. She wasn’t as hungry as before. So the second packet of biryani had a smaller benefit and enjoyment as the first. The third packet of biryani, as before, holds even less utility as the individual is now not hungry anymore.
In fact, the fourth packet of biryani has experienced a diminished marginal utility as well, as it is difficult to consume any further because the individual experiences discomfort upon being full from food. Finally, the fifth packet of biryani cannot even be consumed. The individual is so full from the first four packets that consuming the last packet results in negative utility. The five packets demonstrate the decreasing utility that is experienced upon the consumption of any good. In a business application, an organization may benefit from having three accountants as its staff. However, if there is no need for another accountant, hiring a fourth accountant results in a diminished utility, as little benefit is gained from the new hiring.
About the Author:
The author is from Guwahati, Assam, India. He is a student of business administration in BIMS, Kolkata, West Bengal, India and is a budding entrepreneur.

Dr. Rajesh G. Konnur
Professor, Department of Psychiatric Nursing, Kurji Holy Family College of Nursing, Patna, Bihar, India.
&
Ms. Soumya Kuriakose
Senior Nursing Tutor, Department of Psychiatric Nursing, Kurji Holy Family College of Nursing, Patna, Bihar, India.
CONCEPT AND PHILOSOPHY:
In order to think in depth, about the necessity of mental health promotion strategies along with physical health interventions, among world population, one more Mental Health Day has come. This day aims at global mental health education, awareness and advocacy against social stigma existing about mental diseases and mobilizing efforts in support of mental health. Every year, 10th of October; the World Mental Health Day, World Health Organization (WHO) celebrates with different themes. And this year, mental health of young people is at the central point of discussion with a theme “Young people and mental health in a changing world”. Researches and mental health focused activities begun to run from the end of 19th century onwards, proving that medical world has recognized the significance of general awareness about the prevention of mental diseases and mental health promotion. Following this, governing bodies and health agencies worldwide have started to take steps in regard to this view. All over, physical and mental health has to get equal importance, since there is no health without mental health. A healthy body with a healthy mind together contributes to build a healthy human. Today’s young people are the builders of tomorrow’s nation. They are described as the greatest wealth and strength of any nation. The younger generation, strengthened mentally and physically health wise, can take critical decisions and can bring significant changes in the society. During such a fruitful time period of life, youth must be given special attention and protected from all kinds of mental disturbances.
DEFINITION OF “MENTAL HEALTH”:
“Mental health is defined as a state of well-being in which every individual realizes his or her own potential, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to her or his community.”
World Health Organization (WHO)
INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MENTAL AND PHYSICAL HEALTH:
A healthy mind is the foundation of good health. The overall health of a person depends on his level of well being. Equal importance has to be given to physical health and mental health because of the inseparable relationship between them. There are scientific evidences linking health outcomes with mental and physical fitness. Physical activity increases the flow of oxygen to the brain. It also increases the amount of endorphins, the “feel-good” chemicals in our brain which controls a number of physiological functions. Another example can be that of an optimistic (optimism is a characteristic feature of good mental health) person who is affected with a serious malignant disorder. If he shows a positive attitude towards his sickness, he can bring necessary adjustments towards his sickness. Such an attitude is very crucial in bringing better treatment outcomes. Sometimes, a person’s inability to make adjustments with increasing demands and simultaneously occurring changes in life, can lead to severe mental diseases like chronic depression and schizophrenia. Also, other acute and chronic medical conditions such as heart attack, high blood pressure, diabetes and digestive health have been linked to mental health. It is evident that a person with a mental illness will experience disorder in his overall physical functions because mental illness affects thoughts, state of mind, attitude and occupation negatively. Hence, it became clear that physical health and mental health are interrelated and directly proportional.
COMMON MENTAL HEALTH ISSUES OF YOUTH:
Youth is the transitional phase of growth from childhood to adulthood and is a peculiar time frame with multiple features. This stage is the only stage with a possibility of maximum productivity. During this stage, the young people need good attention and appropriate guidance. Parents and society together has to bring up their children as value rich persons. The following are the major problems the youth may face:
Since youth is the immediate stage after childhood and a preparatory phase to adulthood, the young person may undergo to a variety of problems. One of such alteration is the thought of dependency. In order to fulfill the career requirements, the young ones may have to migrate from their home, to their destinations. That is, the home in which they lived (as almost fully dependent) into a new world where they become completely independent. That is, a sudden change from the level of dependency to a high level of independence.
Developmental psychologist, Erick Erickson describes this phase as the phase in which the young one will re- examine his identity and try to find out exactly “what he is”. During this period, they explore possibilities and begin to form their own identity based upon the outcome of their explorations. Failure to establish a sense of identity within society (“I don’t know what I want to be when I grow up”) can lead to role confusion. Role confusion involves the individual not being sure about themselves or their place in society.
The Academic Career Development Stress is an individualized phenomenon, unique to each student and setting. It is a subjective feeling, which is hard to avoid by students. The sources of academic stress may be life events or chronic strains related to academic programs and workloads. Such stress may elicit fear, tension and other psychosomatic problems and may be associated with a variety of serious negative outcomes in the young students, including suicidal ideation, smoking and drinking. Stress may arise due to the academic demands, adjustments to be done to a new course, medium of instructions, institutional situations or when developing appropriate communication with classmates and teachers etc. In extreme situations, students may seek professional help to cope with the debilitating effects. This type of stress is recognized as the harmful physical and emotional responses that occur when the requirements of the academic activities do not match the capabilities, resources and needs of the students. Academic Career Development Stressors are considered as the student perceived stressors which generally emerge from demands of academic and curriculum environments and resourcefulness (ability, stress, etc.) of the students concerned.
Studies show that peers have a direct influence on building up of youth behavior. A person in the age of youth ever tends to keep bondage with people of same age. This type of influence would become either negative or positive. And if it is a negative influence, it would result into a destructive progression. If it influences positively, it would bring constructive developments in the youth. The relationship with parents did not demonstrate the expected mediation effect, with the exception of the following elements: relation between type of friends and risk behavior; and communication with parent and lesser involvement in violence behaviors and increased well-being. The negative influence of the peer group is more connected to the involvement in risk behaviors, whilst the positive influence is more connected with protective behaviors.
Emotional immaturity and instability is often seen in youth. Emotional immaturity is the inability to handle situations without unnecessarily escalating them. An inability to make interpersonal relationship and bondage with parents and family members, failure in building relationship with teachers and friends etc. are the commonest manifestations of emotional disturbances during youth. A strong desire to know about sex and reproduction, to get an opportunity to practice it and to incline to abusing addictive substances are also very common among this age group. Moreover, a self-withdrawal, hyperactivity, excessive anxiety etc. are also notable features of this category. Even though majority of these problems are transient, must be taken seriously and should be handled carefully.
Over dependence on internet/ social media will put serious impact on mental health. Social media is addictive precisely, because it gives us something, which the real world lacks: it gives us immediacy, direction and value as an individual. There are many young people who cannot control themselves and are addicted to social media. Addiction to social media has many serious effects, including poor study habits, living away from reality and bad health. Young people who are addicted to social media can live far away from reality. Because of using a cell phone all day, they will not have time for outdoor activities such as playing sports or camping. Instead of going out to meet friends or talk to their parents, these people love chatting with friends on social media. They will just stay at home and update their news on social media. They post status or photos to share with their friends on social media. Gradually, they will only live in a virtual world.
While comparing olden living styles and modern system of living it can be seen that family structure and living patterns have changed a lot. People’s attitude and perception about family relationship is also undergoing modifications. Uncontrolled dependence on modern urbanities often brings familial imbalance and mental disturbance. Lack of proper attention and care, impaired communication, unable to get proper guidance in each life stages etc. bring huge behavioral alterations among children and youth. Today’s parents become unable to find out and fulfill their children’s psychological needs. This will influence each stage of the life of those young ones and can throw them into serious mental health issues.
STRATEGIES TO WIDEN THE HORIZONS OF MENTAL HEALTH PROMOTION:
The predominant strategies for Youth Mental Health Promotion include:
Social connectedness was defined as a “crucial” element for mental health promotion among youth. The sense of belonging begins in the family, but it grows the peer group, community, and culture. In their search for identity, purpose and direction, youth need to feel connected to someone or some-thing in order to thrive. Given that social isolation is a determinant of health, promoting connections and a sense of belonging whether in the school system, the community, family or peer group is essential to combating loneliness and creating opportunities to build psychological resiliency. Youth need people, inside and outside of their family, who care about them; who can be non-judgmental listeners; who they can turn to for well-informed guidance and advice; who they can call on for help in solving problems; who encourage them and promote high expectations; and who set developmentally appropriate limits, rules and monitoring.
Youth has to be motivated to constructively engage in social institutions like religious communities and recreational facilities; that are safe, stable and equitable. Such social institutions provide support for youths’ intellectual, social, emotional, moral and physical development and provide opportunities to participate in organized activities like academic enrichment, sports, social clubs, support groups, volunteering and the labor force.
The influence of parents on young one’s life is significant on all ages of their life. Nevertheless, the role of parents in this age is an overall evaluation on youth’s decisions and living style. Parents should correct them appropriately and comment on children’s each individualized decision with a critical mind. It is identified that the family unit is the first and the most critical environment to promote healthy youth development. Parents or primary caregivers are in the position of not only acting as the support system, but also as their teacher in their lives. However, it was acknowledged that many parents lack the resources and/or skills to support child development in an optimal way. They are often contending with stress and the social determinants of health, which may impact on their ability to optimize the environment for children to flourish. This should be a strong emphasis, that working with families to build supportive environments and positive parenting approaches will assist youth in reaching their potential and developing resiliency. As such, the family environment and the role of the parent is an upstream approach for mental health promotion.
The presence of stigma in the larger social context is viewed as a barrier to mental health promotion. Given that mental illness is deeply rooted in our culture as a negative or fear-based condition, the existence of negative attitudes and ignorance to mental illness is pervasive in society. Openly, it is required to discuss the importance of mental health promotion work by focusing on reducing stigmatic attitudes and raising awareness about mental health as part of holistic health. Demystifying mental illness will not only promote a shift in societal attitudes, but will inevitably assist those who are struggling with mental health issues to seek help effectively.
Mental health literacy was identified as a key area of focus for mental health promotion work. Currently, there is inconsistency at an inter sectional level regarding what language is used to define mental health and mental wellness. This lack of shared knowledge is a call for action to enhance mental health literacy across the various sectors. Not only would mental health literacy improve a client’s access to mental health services, but would also shift the focus to understanding positive mental health and its place in mental health promotion. Therefore, the need for a shared language and consistent definition of mental health is apparent and is an important upstream approach. Raising awareness and understanding of mental health and wellness has the ability to reduce stigma and enhance accessibility to services for those who require support.
Youth is called the age or period of turbulence, where every individual goes through certain changes in their mental as well as physical structure. Adolescent counseling is aimed at young people to help them make sense of their feelings, behaviors and thoughts and entails the use of unique techniques. Any parent can attest to the fact that the adolescence stage of any child can be extremely difficult and confusing. Hence, it is very important for parents to handle their adolescent children in the best ways. Thus, these psychological counseling sessions are organized for them and they turn out to be effective, most of the time. Adolescence is the most complicated phase of one’s life. These adolescent counseling sessions focus not only on the patient but also on the patient’s family.
Today’s youth face more stress than ever before. From academic stress including classes, homework, papers, grades and growing competition to family stress including management of parent expectations, conflicts, sibling rivalry and changes in structure, youth feel stress in numerous aspects of their life. Because youth are not equipped with effective relaxation techniques, they sometimes rely on unhealthy responses like illegal drugs and alcohol. Lot of youth is not equipped with the stress management tools to effectively handle the large amounts of stress they face daily. If stress is not managed effectively, it can lead to negative self-talk, anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, aggression, physical illness and illegal drug and alcohol consumption. Awareness about relaxation techniques will certainly bring better mental health outcomes from youth.
Young people need support and guidance in facing the many challenges of today as well as emerging ones. At the same time, youth should be encouraged and actively engaged in addressing societal problems. Youth development programs aim at overall development of youth. Such programs focus on spiritual and ethical developments. It is also expected to enable them to take vital decisions. They have to be encouraged to actively get involved in these programs and helps them to form acceptable behaviors in society.
The social media addiction means a change in behavior manifested as spending increased amount of time online to produce some pleasurable effects, taking away attention from other tasks, experiencing unpleasant feelings from reducing or stopping interaction with social media etc. There is no recognized treatment for social media addiction. Although we are starting to become aware of the problem, there is no classification of social media addiction as a mental disorder in the same way as substance misuse. Youth have to be explained the health impacts of overtime social media usage. They have to be taught to engage in quality work. They have to be made to understand the value of time. They have to be motivated to come out of the world of fantasy and be in the world of realities.
SUMMARY:
Youths are the backbone of social fabric. Development of youth as a person must be comprehensive and humane. An optimal growth helps in overall development. A positive outlook and spirit of healthy living are the main determinants of good mental health. Promotion of mentally healthy living styles contributes for growth of society.
REFERENCES:

Priyanka Agarwal
Abstract:
The world of business is ever changing. This forced accountancy to change itself from time to time in order to maintain its relevance and importance. Hence, there was enough scope to research on the evolution of accountancy.
An applied research was pursued with data collected from secondary sources. This research covered a period of 5,000 years before the first writing to the current era. The conclusion reached was that methods of accountancy have changed over the years but the principles and purposes remain the same.
Key words: Accountancy, double entry book-keeping, chartered accountant, software etc.
Introduction:
The world of business has changed itself from time to time. There was a time when all business activities were based on the barter economy. The seller had to grow/ manufacture/ acquire a commodity and sell it. There were few sellers in the market with a huge number of buyers. Profitability was very high. The entry barriers into business were low at this point of time. This attracted a huge number of entrants in the market. Thus, profitability went down. For the first time, in human history there was competition in the markets. The customer became the ultimate sovereign.
During this journey of business from the Stone Age to the current era of globalization, software, contact development and public relations, accountancy had to adapt to the situation and change itself from time to time. Thus, enough scope was provided for research on evolution of accountancy.
Literature Review:
Evidence Regarding Evolution of Professionalization in Accounting (1996):
An article titled “The Professionalization of Accounting: A Review of Recent Historical Research and Its Implications” was written by Brian P. Westand first published on May 1, 1996.
This paper reviews and considers the possible implications of a significant body of historical research that has gathered momentum throughout the last decade and challenged conventional explanations for accounting’s professional status. In place of traditionally espoused professional ideals, such as altruism, ethical behavior and control of specialized knowledge, this research has drawn attention to the importance of factors such as social class, gender and political acuity in explaining both the closure of the accounting profession and its elevation within the vocational continuum. If such factors are the foundation upon which the profession of accounting was constructed, then observable and persistent discord in accounting practice and theory is perhaps not unexpected. Further, the story told by recent research invites a rethinking of the nature of the accounting profession’s privileged status.
Evidence About Income Determination & Diversities in Accounting (2014):
Angus O. Unegbu of Department of Business and Management Sciences, University of Kurdistan Hewler, Iraq, pursued a research on evolution and developments of income determination and diversities in use. On the basis of this an article titled “Theories of Accounting: Evolution & Developments, Income – Determination and Diversities in Use” was written and published in Research Journal of Finance and Accounting.
In this article the writer wrote that accounting frameworks follow stipulations of existing accounting theories. This exploratory research sets out to trace the evolution of accounting theories of Charge and Discharge Syndrome and the Corollary of Double Entry. Furthermore, it dives into the theories of Income Determination, garnishing it with areas of diversities in the use of Accounting Information while review of theories of recent growths and developments in Accounting are not left out. The method of research adopted is exploratory review of existing accounting literature. It is observed that the emergence of these theories exist to minimize fraud, errors, misappropriations and pilfering of corporate assets. It is recommended that implementation prescriptions of these theories by International Financial Reporting Standard Committee and Practicing Accountants should be adhered to and simplified so as to avoid confusing and scandalous reporting of financial statements.
Research Methodology:
This research is not a first of its kind. The main purpose of this research is to apply the knowledge generated out of it for further research on the topic. So it is an example of applied research.
The data required has been collected from secondary sources like books, magazines, research articles on the same topic or related topics.
Analysis and Conclusions:
Accountancy is the process of comprehensive recording of financial transactions and analyzing them to understand the behavior of the business. It is a business necessity for many reasons like to –
Frater Luca Pacioli, the father of accountancy, wrote a book known as ‘Summa de Arithmetica Geometria Proportional de Proportionalita’. This book included comprehensive summary of Renaissance mathematics. It also contained a section on accountancy. It was the first ever published description of the double entry book-keeping system. However, not all credit of development or creation of accountancy could be given to Pacioli because accountancy is an age old practice. Pacioli just presented the first published description of the practice.
In prehistoric times, people had to account for food and clothing to sustain their families. Earliest currency was made out of stone which could be used in exchange of commodities like grains. These methods were used for over 5000 years before the first writing.
In ancient Mesopotamia, circa 3500 BC, accountancy was carried out in a different manner. The Assyrian, Chaldeans – Babylonian and Sumerian civilizations flourished in trade and commerce and had more than one banking firm. These firms employed standard measures of gold and silver and extended credit in some transactions. The Babylonian dynasty also gave the renowned code of Hammurabi which stated that an agent selling goods for a merchant must give the merchant a price quotation under seal or face invalidation of a question agreement. In those times, Scribes were the closest thing to accountants.
In the Mauryan empire of India, Chanakya wrote a manuscript similar to a financial management book called ‘Arthashastra’.
Therefore, any view of accounting history that Luca Pacioli had given has a long evolution of accounting systems in ancient and medieval times.
Modern accountancy started developing in Scotland around 1800 AD. The Edinburgh society in England and Scotland adopted the title of the “Chartered Accountant” to identify its members. These members were certified public accountants. By 1921 all 50 states of U.S.A. adopted this concept and soon it spread throughout the world.
In 1973, the Financial Accounting Standard Board was founded with a goal to establish standard of financial accounting and reporting. Such standards are important for people who rely on credible or comparable information about finances.
Today, after so many modifications in the system of accounting, computers play an important role in accounting. Software has been developed for easy and efficient accounting.
Throughout the years the methods have changed but the principles and purposes remains the same.
Bibliography:
Author’s Profile:
The author, Miss Priyanka Agarwal, is an 11th standard student of commerce from Salt Lake City, Kolkata, India. She is an aspiring accountant.

Rajesh G. Konnur & Sangita Singh
Abstract:
The first written record of the word “education” is found in 1530s. It comes from the Latin word “educare” (meaning: to educate, to train, to rear, to bring up) as well as the words ‘educatio’ and “educationis”, which signify “bring up” or “rearing”. Education propels growth of an individual and ultimately leads to self-realization i.e. highest epitome of “knowledge” or “peace”.
Key Words: Education, peace, knowledge,
Definition and Meaning of Peace:
The concept of peace has an important cultural dimension. Traditionally it is linked as with inner peace (peace existing in our minds or hearts) by our philosophers. Western world views peace as to be outside the individual (absence of war or violent conflict). For example, in India the word peace is “Shanti” and implies “a perfect order of the mind” or “peace of mind”. Gandhiji based his philosophy and strategy on a concept called Ahimsa, which means broadly to refrain from anything harmful. He said, “… literally speaking, Ahimsa means non-violence. It means that you may not offend anybody; you may not harbor uncharitable thoughts, even in connection with those who consider you as an enemy.” In the Maya tradition, peace refers to the concept of welfare; it is linked to the idea of a perfect balance between the different areas of our lives.
A great Norwegian Scholar of Peace, John Galtung defines peace as the absence of structural violence. Structural violence is a form of discrimination against individuals and groups in a society.
Positive peace means no war or violent conflict combined with a situation where there is equity, justice and development.
Negative peace means that there is no war; no violent conflict between states or within states or nations.
We would summarize these two concepts in the following way:
No war = Negative peace
No war + Social justice/ development = Positive peace
Relationship between Education and Global Peace:
Education is perhaps the most important tool for human development and the eradication of poverty and ill spirits within society. It is the means by which successive generations develop the values, knowledge and skills for their personal health and safety and for future political, economic, social and cultural development. This may be one reason why the MDGs place so much emphasis on achieving universal, free and compulsory education through Education for All (EPA).
Education is the foundation of a peaceful society. It builds literacy, respect, dignity and opportunity for all. On a planet of 7.3 million, peace education i.e. education that specifically promotes respect, empathy, and mutual understanding and conflict management skills, is more crucial than ever. This is even truer in developing countries where often more than 45% of the population is under 14 and children who crave for a peaceful live amid conflict.
The goal of education should be the full flowering of the humans on this earth. According to a UNESCO study “… the physical, intellectual, emotional and ethical integration of the individual into a complete man/ woman is the fundamental aim of education. The goal of education is also to form children into human persons committed to work for the creation of human communities of love, fellowship, freedom, justice and harmony.”
According to James Ross, “The aim of education is the development of valuable personality and spiritual individuality”. The true aim of education cannot be other than the highest development of the individual as a member of the society. Let education burn the individual flame, feeding it with the oil of society.
Interrelationship between Nursing Education/ Practice and Global Peace:
Education is a process which draws out the best in the child or student with the aim of producing well – balanced personalities, culturally alert, morally upright, vocationally self- sufficient and internationally liberal.
Nursing is a dynamic, therapeutic and educative process. It responds to physical, psychological, social, economic and spiritual aspects of human beings. It is a helping profession and always upholds the dignity of human values and spirit of love and peace. The core aspects of nursing are care, cure and co-ordination. This is applicable not only in case of human beings but also beyond living things.
Violent conflict has a grave impact on human health and wellbeing. Violence (inter, intra, external) affects the humans and globally all. Morbidity and mortality are due to the direct or indirect consequences of conflict related to displacement from homes and barriers in access to food, shelter, clean water, sanitation facilities and professional health care.
Nursing profession was profoundly influenced by nursing leaders who provided care during war. Nursing interventions during war were an important stage in helping nursing defines its mission and domain of knowledge that brought peace among the various communities.
In recent years, nursing profession has been championed as a” bridge for peace” with the potential to reduce conflict through a variety of interventions. However, nurses working in situations of violent conflict practice under a range of domains including humanitarian relief, human rights promotion and health sector development.
World Health Organization (WHO) argues that prevention of violent conflict is an important component of health. Good public health practice requires identifying risk factors and determinants of collective violence and developing approaches to resolve conflicts without resorting to violence. In this case, nursing/ nurses have to urge governments to abide by international agreements and solve conflicts nonviolently. This declares nursing’s respect for human life and dignity.
In this era of globalization and power struggling attitude, the environment has been unsafe and unhealthy to live. Now the time has come to transform the society toward a more non- violent and harmonious culture. This includes educating ourselves and others about the effects of war and weaponry, political advocacy and conducting research into the suffering associated with war.
Peace is a dynamic, bio-psychosocial construct. Nursing deals with prevention, care and promotion of health and well being. The extended and expanded roles of nurses have in -depth responsibilities in uplifting human kindness and ultimately bring peace in an individual, family and at large globally. The nursing programmes are designed to make a ‘life’ a better and peaceful one.
Conclusion:
Peace is a dynamic state of mind. It is intrinsic and also extrinsic in nature. Nurses and nursing education can strengthen the global peace mission by collaborative work and ethics.
References:
Dr. Rajesh G. Konnur
The earth’s climate is changing rapidly. People are talking about ‘rising temperature’ in natural environments. Every year rising temperatures, rising sea levels and rising fossil fuel emissions are causing global threats to individuals as well as to the natural environment as a whole. It has tremendous impact on bio-psychosocial life conditions.
Climate change is much more than just rise in temperature. It is more than an environmental issue. It has become a socio-psychological & politico- administrative propaganda in the global scenario.
Etiology of Climate Change:
There are two main causes of climate change: natural causes & human created causes. Natural causes have influenced the earth’s climates such as volcanic eruptions, ocean current, earth’s orbital changes and solar variations. The eruptions of volcanoes cause a cooling effect on the earth. When the volcano erupts it throws out large volumes of sulphur dioxide (SO2), water vapor, dust and ash into the atmosphere. The sulphur dioxide gas reaches the upper level of the atmosphere. The tiny particles, dusts & ashes block the incoming sun rays & this leads to cooling of the atmosphere.
One more reason of natural cause for climate change is ocean current. The ocean is the major component of the climate system. It covers 71% of the earth & absorbs about twice as much as of the sun’s radiation as the atmosphere or the land surface. Winds push horizontally against the sea surface & drive ocean current patterns. These also help to restore carbon dioxide. The changes in ocean circulation will affect the climate through the movement of CO2 into or out of the atmosphere. Another reason for climate change is the earth’s orbital changes. The earth makes one full orbit around the sun every year. If there is no tilt we will not experience seasons. Changes in the tilt of the earth can affect the severity of the seasons. For example, if there is more tilt means we will experience warmer summers and colder winters. Similarly, if there is less tilt it means we will experience cooler summers & milder winters.
Over the last 50 years, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels have released sufficient quantities of CO2 and other greenhouse gases to trap additional heat in lower atmosphere & affect the global climate.
In the last 130 years, the world has warmed by approximately 0.850 C. Each of the last 3 decades has been successively warmer than any preceding decade since 1850.
Now, sea levels are rising, glaciers are melting & precipitation patterns are changing. Extreme weather events are becoming more intense and frequent. Climate change is much more than an environmental issue. It poses a serious threat to our health & survival. It impacts all of us, no matter where we live. The health of humanity is directly related to the health of our environment. We depend on our environment for everything. Our environment gives us the air we breathe, the food we eat and the water we drink.
Climate change is not a futuristic scenario that is unlikely to happen in our life time. People are feeling its impact right now in many parts of the globe. A heat wave in the summer of 2003 in Europe caused more than 30,000 deaths and was considered the worst natural disaster in Europe over a period of time. The 2017 Atlantic hurricane season caused unprecedented levels of destruction across the Caribbean. Hurricane Irma was the most powerful ever recorded over the Atlantic. Hurricanes Jose & Maria threatened areas already devastated by Irma.
By 2030, climate change is predicted to cost 2-4 billion U.S. dollars in direct health expenses each year.
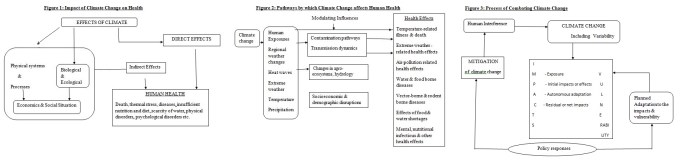
Impact of Climate Change on Health:
Global climate change directly and indirectly contributes to the spread of diseases & premature mortality. Below is presented a pictorial form of the effects of climate change. Figure 1
Potential Health Impacts of Climate Change:
Change in world climate would influence the functioning of many ecosystems & their member species. Some of the climate change is beneficial. For example, milder winters reduces the seasonal winter time peak in deaths that occurs in temperate countries while in hot regions a further increase in temperatures reduce the viability of the disease transmitting mosquito populations. Overall, however most of the heat impacts of climate change are adverse in nature. According to WHO health report (2012), that climate change was estimated to be responsible for approximately 2.8% of the world wide diarrhea and 8% of malaria in middle income countries.
The first detectable changes in human health may well be alterations in the geographic range (latitude and altitude) and seasonality of certain infectious diseases including Vector Borne infections such as malaria and dengue fever, and food borne infections (Salmonellosis) which peak in the warmer month. Warmer average temperatures combined with increased climatic variability would alter the pattern of exposure to thermal extremes and resultant health impacts.in both summer and winter. By contrast the public health consequences of the disturbance of natural and managed food producing ecosystems, rising sea levels and population displacement for reasons of physical hazard, land loss, economic disruption and civil strife may not become evident for up to several decades.
Adaptive actions reduce health impacts in terms of public health categories of primary, secondary and tertiary prevention. Primary prevention refers to an intervention implemented before there is evidence of disease or injury, avoiding hazardous exposure, removing causative risk factors or protecting individuals so that exposure to the hazard is of no consequence. For example, use of bed nets to prevent malaria. Primary prevention largely corresponds to anticipatory adaptation.
Secondary prevention involves intervention implemented after disease has begun, but before it is symptomatic (example: early detection or screening) and subsequent treatment that averts full progression to disease. Examples include enhancing, monitoring and surveillance, improving disaster response and recovery and strengthening the public health system’s ability to respond quickly to disease outbreaks. Secondary prevention is analogous to reactive adaptation. Finally, tertiary prevention attempts to minimize the adverse effect of an already prevalent or injury (for example better treatment of heat stroke, improved diagnosis of vector borne diseases). As the adverse health outcome is not prevented, tertiary prevention is inherently reactive.
Coping with climate:
In popular literature global climate change frequently is called “global warming” which focuses attentions on average global temperature change. However, a change in climate actually occurs as changes in particular weather condition, including extremes in specific places. Adaptation to climate change necessarily includes adaptation to variability. Figure 2:
Combating Climate Change : Figure 3:
Process of Combating Climate Change
The various measures of combating climate change are as follows:
Role of Nurses in Climate Change:
Adaptation to climate has always included “physiological acclimatization, behavioral strategies (such as clothing, scheduling daily work & seasonal migration), technical measures (such as building design and air conditioning) & institutional mechanisms (e.g. disaster preparedness schemes). What is changing now is the pace of climate change which may overcome the capacity of populations to adapt.
Nurses have a role to play in advocating for action to reduce societal inequities, strengthen public health infrastructure, promoting behavioral strategies that foster adaptation to change, promoting positive change adaptations to major life changes, such as the birth of the child or the diagnosis of a chronic illness. Nurses working in communities have to address various stressors. This same expertise can be used to support adaptation to climate change in a way that promotes and maintains the health of the individuals, families and communities. The other roles are:
References:

Rajesh G. Konnur & Sangita Singh
Abstract: The first written record of the word “education” is found in 1530s. It comes from the Latin word “educare” (meaning: to educate, to train, to rear, to bring up) as well as the words ‘educatio’ and “educationis”, which signify “bring up” or “rearing”. Education propels growth of an individual and ultimately leads to self-realization i.e. highest epitome of “knowledge” or “peace”.
Key Words: Education, peace, knowledge,
Definition and Meaning of Peace:
The concept of peace has an important cultural dimension. Traditionally it is linked as with inner peace (peace existing in our minds or hearts) by our philosophers. Western world views peace as to be outside the individual (absence of war or violent conflict). For example, in India the word peace is “Shanti” and implies “a perfect order of the mind” or “peace of mind”. Gandhiji based his philosophy and strategy on a concept called Ahimsa, which means broadly to refrain from anything harmful. He said, “… literally speaking, Ahimsa means non-violence. It means that you may not offend anybody; you may not harbor uncharitable thoughts, even in connection with those who consider you as an enemy.” In the Maya tradition, peace refers to the concept of welfare; it is linked to the idea of a perfect balance between the different areas of our lives.
A great Norwegian Scholar of Peace, John Galtung defines peace as the absence of structural violence. Structural violence is a form of discrimination against individuals and groups in a society.
Positive peace means no war or violent conflict combined with a situation where there is equity, justice and development.
Negative peace means that there is no war; no violent conflict between states or within states or nations.
We would summarize these two concepts in the following way:
No war = Negative peace
No war + Social justice/ development = Positive peace
Relationship between Education and Global Peace:
Education is perhaps the most important tool for human development and the eradication of poverty and ill spirits within society. It is the means by which successive generations develop the values, knowledge and skills for their personal health and safety and for future political, economic, social and cultural development. This may be one reason why the MDGs place so much emphasis on achieving universal, free and compulsory education through Education for All (EPA).
Education is the foundation of a peaceful society. It builds literacy, respect, dignity and opportunity for all. On a planet of 7.3 million, peace education i.e. education that specifically promotes respect, empathy, and mutual understanding and conflict management skills, is more crucial than ever. This is even truer in developing countries where often more than 45% of the population is under 14 and children who crave for a peaceful live amid conflict.
The goal of education should be the full flowering of the humans on this earth. According to a UNESCO study “… the physical, intellectual, emotional and ethical integration of the individual into a complete man/ woman is the fundamental aim of education. The goal of education is also to form children into human persons committed to work for the creation of human communities of love, fellowship, freedom, justice and harmony.”
According to James Ross, “The aim of education is the development of valuable personality and spiritual individuality”. The true aim of education cannot be other than the highest development of the individual as a member of the society. Let education burn the individual flame, feeding it with the oil of society.
Interrelationship between Nursing Education/ Practice and Global Peace:
Education is a process which draws out the best in the child or student with the aim of producing well – balanced personalities, culturally alert, morally upright, vocationally self- sufficient and internationally liberal.
Nursing is a dynamic, therapeutic and educative process. It responds to physical, psychological, social, economic and spiritual aspects of human beings. It is a helping profession and always upholds the dignity of human values and spirit of love and peace. The core aspects of nursing are care, cure and co-ordination. This is applicable not only in case of human beings but also beyond living things.
Violent conflict has a grave impact on human health and wellbeing. Violence (inter, intra, external) affects the humans and globally all. Morbidity and mortality are due to the direct or indirect consequences of conflict related to displacement from homes and barriers in access to food, shelter, clean water, sanitation facilities and professional health care.
Nursing profession was profoundly influenced by nursing leaders who provided care during war. Nursing interventions during war were an important stage in helping nursing defines its mission and domain of knowledge that brought peace among the various communities.
In recent years, nursing profession has been championed as a” bridge for peace” with the potential to reduce conflict through a variety of interventions. However, nurses working in situations of violent conflict practice under a range of domains including humanitarian relief, human rights promotion and health sector development.
World Health Organization (WHO) argues that prevention of violent conflict is an important component of health. Good public health practice requires identifying risk factors and determinants of collective violence and developing approaches to resolve conflicts without resorting to violence. In this case, nursing/ nurses have to urge governments to abide by international agreements and solve conflicts nonviolently. This declares nursing’s respect for human life and dignity.
In this era of globalization and power struggling attitude, the environment has been unsafe and unhealthy to live. Now the time has come to transform the society toward a more non- violent and harmonious culture. This includes educating ourselves and others about the effects of war and weaponry, political advocacy and conducting research into the suffering associated with war.
Peace is a dynamic, bio-psychosocial construct. Nursing deals with prevention, care and promotion of health and well being. The extended and expanded roles of nurses have in -depth responsibilities in uplifting human kindness and ultimately bring peace in an individual, family and at large globally. The nursing programmes are designed to make a ‘life’ a better and peaceful one.
Conclusion:
Peace is a dynamic state of mind. It is intrinsic and also extrinsic in nature. Nurses and nursing education can strengthen the global peace mission by collaborative work and ethics.
References: